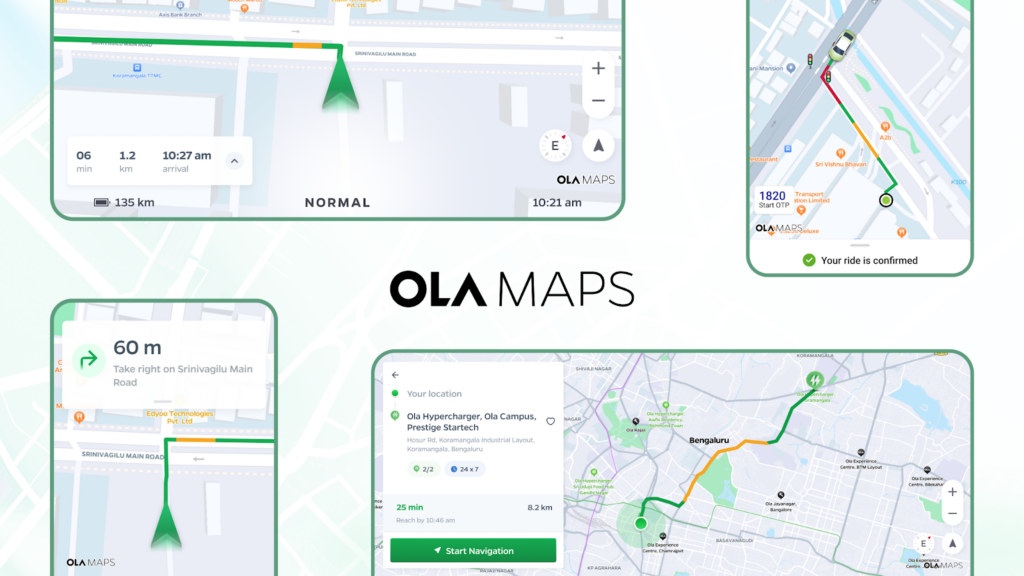
Navigating India – The Journey of Ola Maps
1. Background
At Ola, as we’ve grown from a ride-hailing app to building our own EVs to a consumer platform, we’ve come to realize that for powering mobility, Maps is not just a feature – it’s foundational to everything we do.
Maps are the beating heart of all consumer apps. They’re not just about getting from point A to point B; they’re about understanding the intricate web of streets, traffic patterns, and urban landscapes that define our cities. In 2021, we had big plans to build first to world features on our customer and partner apps that would transform the user experience, but we quickly hit a roadblock. Our reliance on Western mapping providers, for whom India wasn’t a top priority, severely limited our ability to implement these features. This limitation highlighted the crucial need for a mapping product tailored to our market.
We realized that to truly serve our users and push the boundaries of mobility, we needed a true alternative to global mapping giants—one that was not only better suited for the Indian market but also more responsive to our unique needs. This realization sparked the inception of Ola Maps.
But why build our own maps when there are existing solutions?
The answer lies in our vision for the future of commerce and transportation. We’re not just building maps for today; we’re creating the cartographic infrastructure for tomorrow’s transportation innovations. From autonomous vehicles to flying taxis, the future of mobility demands maps that are more detailed, more dynamic, and more intelligent than ever before.
Furthermore, existing maps do not fully address unique challenges related to delivering a seamless experience for Indian users and the opportunity it creates for Ola and Indian developers.
Challenges
- Incomplete Mapping Coverage: Many streets and rural areas are not mapped or poorly mapped.
- Inconsistent and Varying Street Names: Street names often have variations and inconsistencies, leading to confusion.
- Frequent Changes in Road Networks: New streets are created, and existing ones are closed frequently, leading to outdated maps.
- Traffic and Road Condition Variability: Traffic patterns are highly inconsistent, and road conditions vary significantly due to potholes and non-standard streets.
- Non-Standardized Streets: Many streets do not conform to standard measurements and layouts.
- Potholes and Road Quality Issues: Potholes and road quality can significantly affect travel time and safety.
Opportunities
- Enhanced User Experience: Providing accurate and up-to-date maps can significantly enhance navigation and travel planning, improving user satisfaction.
- Localized Features: Offering features tailored to local needs, such as multi-language support, local business listings, and culturally relevant landmarks.
- Smart Navigation Systems: Developing smart navigation systems that can suggest optimal routes based on real-time data, considering traffic, road conditions, and user preferences.
- Integration with Smart City Initiatives: Collaborating with smart city projects to integrate mapping data with other urban infrastructure, enhancing overall city management and services.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Navigation: Utilizing AR to provide intuitive and immersive navigation experiences, especially in complex urban environments.
- Real-time Predictions: Using state of the art time series models to foresee traffic congestion, road closures, and other disruptions, offering proactive routing suggestions.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with local communities to crowdsource map updates and feedback, ensuring the map remains relevant and accurate.
- Eco-friendly Routing: Implementing eco-friendly routing options that minimize fuel consumption and emissions, appealing to environmentally conscious users.
- Real-time Data Updates: Implementing real-time data updates through IoT devices, GPS tracking, and user-reported changes can keep maps current.
Addressing these unique challenges is not easy. In order to address and tap the opportunities, we are leveraging the power of AI by developing and using state of the art Krutrim models for delivering contextually relevant, accurate, safer and enhanced customer experience.
What’s even more exciting is that we’re doing this from India, leveraging the country’s vast pool of tech talent to create cutting-edge mapping technology at a fraction of the cost. This approach not only allows us to be more efficient but also ensures that our maps are built with a global perspective from the ground up.
We embarked on this ambitious journey three years ago, recognizing that to truly revolutionize mobility, we needed to own and innovate on every aspect of the maps experience that power our platform.
This post kicks off our 4-part series on Ola Maps. Here is what’s coming:
Part 1: The Foundation of Ola Maps (You are here)
Part 2: The Data Behind the Maps
Part 3: The AI Revolution in Mapping
Part 4: The Future of Maps
In the following sections in this blog, we’ll dive deeper into the technology behind Ola Maps, the challenges we’ve overcome, and how this initiative is set to transform not just Ola, but the entire mobility landscape. Stay tuned as we map out the future.
2. Ola Maps Overview – Core Foundations
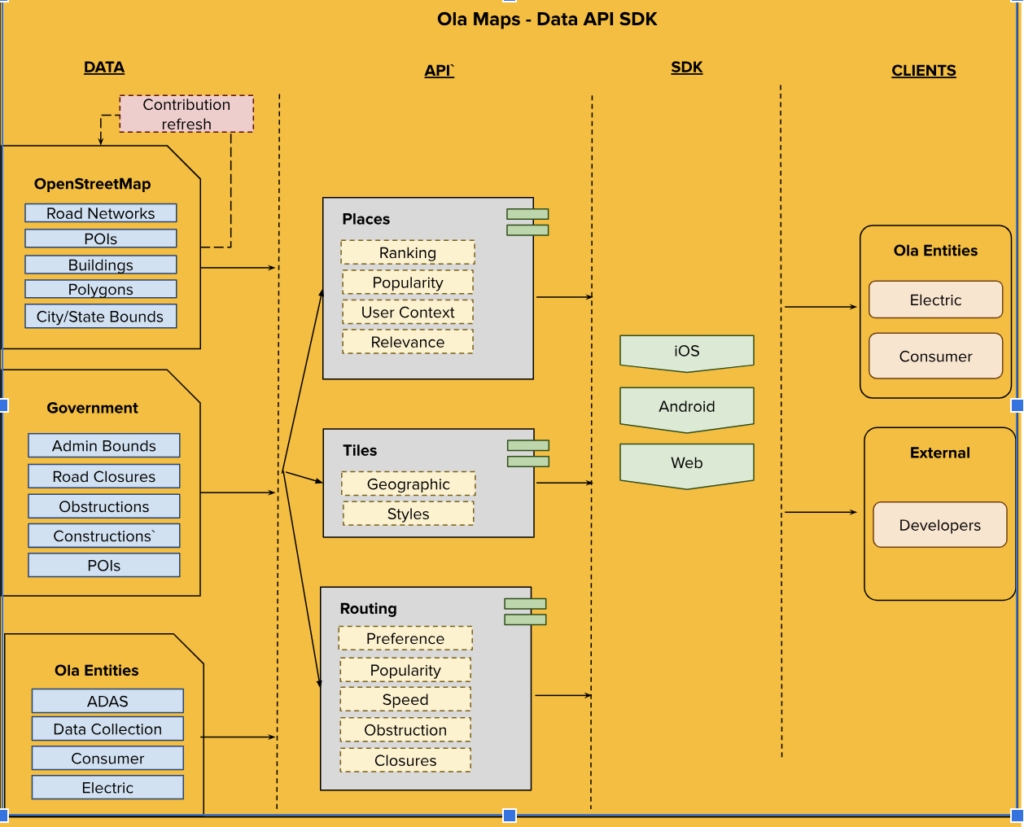
Ola Maps utilizes OpenStreetMap (OSM), government and proprietary sources to focus on building essential map features such as roads, points of interest, and traffic signals. Our base map includes detailed information on land use, water bodies, transportation networks, and more. We enhance these maps with advanced routing services that provide distance calculations, directions, and estimated time of arrival (ETA). The SDKs on Android, iOS, and web platforms, are customized for Electric and mobility clients enabling us to deliver experiences native to the respective platforms. This integration grants access to our extensive mapping services and comprehensive content.
Ola Maps has made significant contributions to the community over the years. We have used near real-time signals from the Ola Platform along with a robust sourcing strategy for Map expansion and Map maintenance. We have contributed a total of 5.43M edits shared with the community.
Open Source Models | Use Case | License |
|---|---|---|
Maplibre (Including Mapbox & Map-tiler) | Rendering (Tile rendering, Marker rendering, Feature and style rendering, real time route rendering) | BSD2_clause |
OSRM | Routing (MLD, Snap2Road) | BSD2_clause |
Pelias | Search (Autocomplete API Structure) | MIT |
OSM | Data layers* (Road,POI,polygons,cartos,Administrative areas, Traffic Signs, Traffic Signals, Buildings) | CCA |
Ola Maps is contributing back to the Community: Since inception of Ola Maps, have been actively using Open Street Maps as a foundation for map feature coverage and freshness where we have ~36% data edits contributed back to the community.
2.1 Ola Maps Ecosystem Explained:
2.1.1 Data Sources:
- OSM: OpenStreetMap data, including road geometries and POIs, is integrated.
- Government Data: Includes official data sources for enhanced accuracy.
- Ola Proprietary Data: Internal data collected and maintained by Ola collected through sensor fusion from vehicles, signals from our fleet of drivers and community feedback from Ola’s active community
2.1.2 Data Enrichment:
- Street and POI names are added in Indic languages.
- Developed and leveraged Named Entity Recognition (NER) models, semantic and syntactic parsers to further enhance accurate POI names
- POI attributes such as traffic signals, hypercharges, flyover metadata, and toll information are included.
2.1.3 Data Integration and Processing:
- All the aforementioned data sources feed into Ola Inhouse Data repository.
- Duplications and normalizations are performed to maintain unique and consistent POI names
2.1.4 Various models process this integrated data:
- Vehicle Pings from EV and Ola Consumer App: Used for predicting speed for road segments, road identifications, road closures and blockers.
- Model for Identifying Road Closures: Enhances routing accuracy by identifying temporary and permanent road closures.
- Model for Predicting Historical Speed: Analyzes historical data and leverages neural network based time series models to predict road speeds.
- Model for Generating Road Popularity: Determines road preferences based on popularity and usage data.
- Model for Search Relevancy Ranking: Enhances search results based on relevance by using state of the art mBERT (multilingual encoder) based Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Learning to Rank (LTR) models.
- Model for Identification of Contextual Searches: Understands and processes context-based search queries. This is done by syntactic and semantic search models like Bi-LSTM-CRF.
- Model for Popularity of POIs and Classification: Ranks and classifies POIs based on their popularity.
2.1.5 Core Components:
- Routing Engine: Uses the processed data and time series Neural Networks to compute optimal routes.
- Tiles: Generates map tiles for visual representation.
- Places: Manages POI data and supports search functionalities. with:
2.1.6 Consumer Applications:
The processed data and routing functionalities are accessible through:
- Maps SDK for iOS: Enables iOS applications to utilize Ola Maps services.
- Maps SDK for Android: Provides similar functionalities for Android applications.
- Consumer Interfaces:
- Ola Consumer: End-user application for navigation and other map services.
- Ola EV: Specialized interface for electric vehicle users.
This structured and integrated approach (Refer Fig.1) ensures that Ola Maps delivers accurate, real-time, and contextually relevant navigation and mapping services to its users across various platforms.
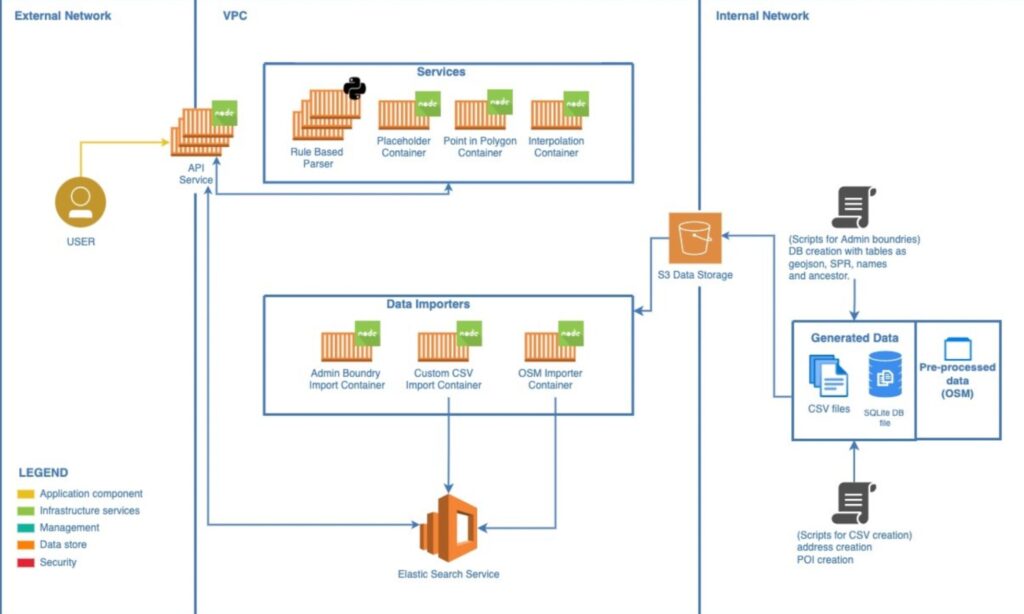
Fig 1: E2E overview of Map ecosystem where we have disparate sources being used to build Map data layers exposed via Services/SDK’s.
2.2 Ola Maps Places
Our system processes geographic datasets using various importers to populate Elasticsearch indices. These importers include:
- OSM Importer: Imports nodes and ways from Ola Maps data.
- Admin Importer: Handles importing administrative areas (localities, cities, states, regions).
- CSV Importer: Imports custom or proprietary data from CSV files.
Elasticsearch serves as our main datastore, handling query heavy lifting and powering search results.
The geocoding services comprise several components:
- API Service: Defines the Places API and interfaces with Elasticsearch and other services to execute queries.
- Placeholder Service: Manages relationships between administrative areas (e.g., cities, states) that Elasticsearch doesn’t handle well natively.
- PIP Service: Efficiently determines which administrative area polygons a given point falls within for reverse geocoding.
- Libpostal/Parser: Uses machine learning to parse addresses accurately.
- Interpolation Service: Provides estimated addresses for queries by leveraging extensive knowledge of addresses and streets, supplementing direct Elasticsearch data.
- Together, these components enable precise and efficient geospatial searches and geocoding, offering robust services for various user queries.
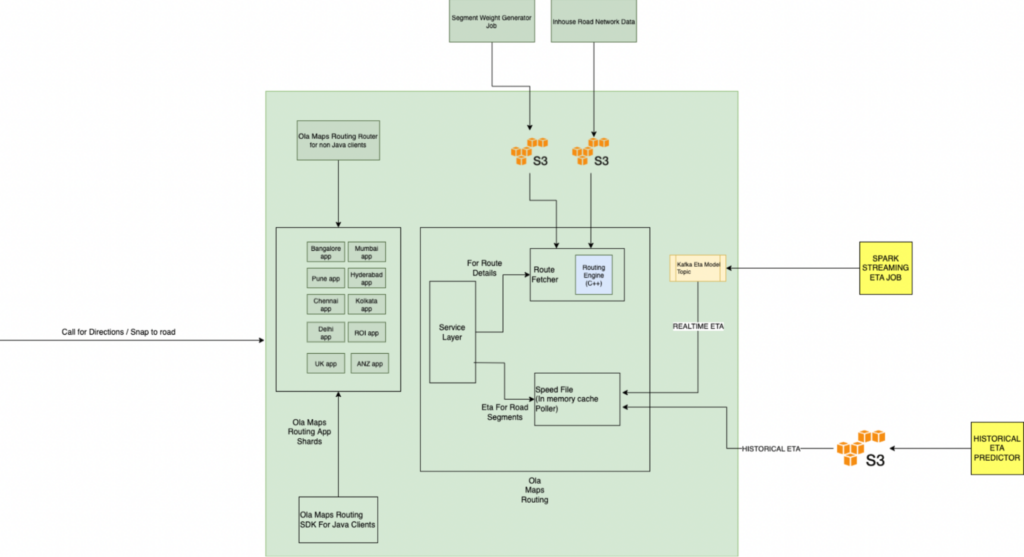
Fig 2: E2E overview of Ola Maps Places Service.
2.3 Ola Maps Routing
- Ola Maps Routing Service is sharded based on geographical boundaries
- Routing Service has 2 micro services –
- Route Fetcher – It fetches the possible routes from origin and destination by calling the Routing Engine. Routing Engine takes three inputs –
- Inhouse Road Network data which consist of data from various sources like OSM, Ola Proprietary data etch
- Weighted scores for road network which helps in generating the route preferences
- Road closures/blockage informations
- Speed Aggregator – It fetches the speed for all the possible routes for the corresponding road segments –
- Realtime Speed – Real Time speed is consumed directly from Kafka. The data into kafka is pushed by the ETA Predictor job
- Historical Speed – Historical data is present in s3 which is pushed by the Historical ETA Predictor Job
- Route Fetcher – It fetches the possible routes from origin and destination by calling the Routing Engine. Routing Engine takes three inputs –
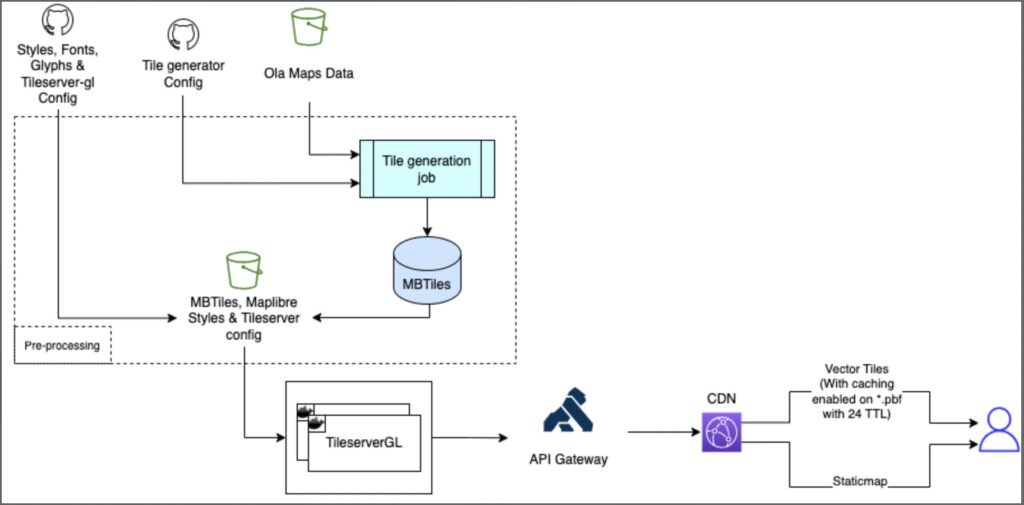
Fig 3: E2E overview of Ola Maps Routing Service
2.4 Ola Maps Tiles
In Ola Maps, each feature is described by geometries (e.g., a river’s shape) with attached attribute data (e.g., a river’s name). Geometries are represented using three elements: nodes (points), ways (lines connecting points), and relations (collections of points or ways forming a larger entity). Attributes are described as tags that can be associated with nodes, ways, or relations.
MBTiles is a file format designed for storing tilesets, allowing the packaging of many files into a single tileset. A tileset can include administrative boundaries, road networks, POIs, and other geospatial information from various sources. MBTiles is based on the SQLite database and can contain raster or vector tilesets.
Tileserver creates a map instance on the server-side using the @maplibre/maplibre-gl-native library with local styles, fonts, sprites, and MBTiles tilesets from a container. This setup is used for rendering the base map of static map images. A transparent image with markers, polylines, and a watermark is generated using the node-canvas library, which is then overlaid on the base map image to produce the final map output.

Fig 4: E2E overview of Ola Maps Tiles Service.
3. Impact of Ola Maps on Customer Experience
3.1 Ola Electric
At Ola Electric, Ola Maps is used extensively by customers for navigation with 1M search queries/week. Ola Maps was the top-rated feature in a recent NPS survey for MoveOS4. Everyday thousands of customers use Ola Maps on their scooters and the Ola Electric app for a guided commute to places in their cities.
Here’s what Ola Electric customers love about Ola Maps:
3.1.1. Traffic Updates:
< Customer Testimonials >
“I love the real-time traffic updates on Ola Maps. They are more accurate than other Maps products that I was using, which saves me a lot of time.”
“Real-time traffic updates on Ola Maps are a game-changer. I can avoid congested areas effortlessly.”
“I find Ola Maps to be more reliable in providing real-time traffic updates compared to other apps.”
3.2.2. Searches and Places location coverage and accuracy:
< Customer Testimonials >
“I’ve found a few locations on Ola Maps that were missing on other Maps. It’s great to see such accuracy!”
“Ola Maps has really impressed me with its precision. The navigation is smooth and the directions are spot on.”
“I’ve noticed that Ola Maps has captured several local spots better than other Maps products. Kudos to the team!”
“The ability to transfer locations from my phone to my scooter with Ola Maps is fantastic. It’s a big time-saver.”
3.2.3. Maps interface and integration with scooter:
< Customer Testimonials >
“This is how you share a location from WhatsApp or any other app to your scooter’s dash through the Ola companion app.I envision myself utilizing Ola Maps for navigation much more often than Google Maps, thanks to this convenient feature.”
“The user interface of Ola Maps is so clean and easy to use. It makes navigation a breeze.”
“I appreciate how Ola Maps integrates seamlessly with my Ola scooter. It’s a perfect match!”
“The feature to search the location on my phone and transfer it to my Ola scooter is incredibly convenient.”
“So far, my experience with Ola Maps has been nothing but positive. It’s intuitive and reliable.”
“Ola Maps is very user-friendly. Even my parents find it easy to use, which says a lot!”
“The integration of Ola Maps with Ola scooters is genius. It makes the whole travel experience seamless.”
3.2.4. Turn-by-turn instructions and navigation:
< Customer Testimonials >
“I just used Ola maps in my S1 Pro and it’s working very well in Pune… UI shows so much details… I would have missed the turn on Google maps but not on Ola… Seeing signals in the map UI for the first time…”
“The turn-by-turn navigation on Ola Maps is excellent. It keeps me on track without any confusion.”
“I’ve had a great experience with Ola Maps so far. It’s accurate and gets me to my destination without any hassle.”
“The detailed mapping and accurate routes on Ola Maps have made my trips so much smoother.”
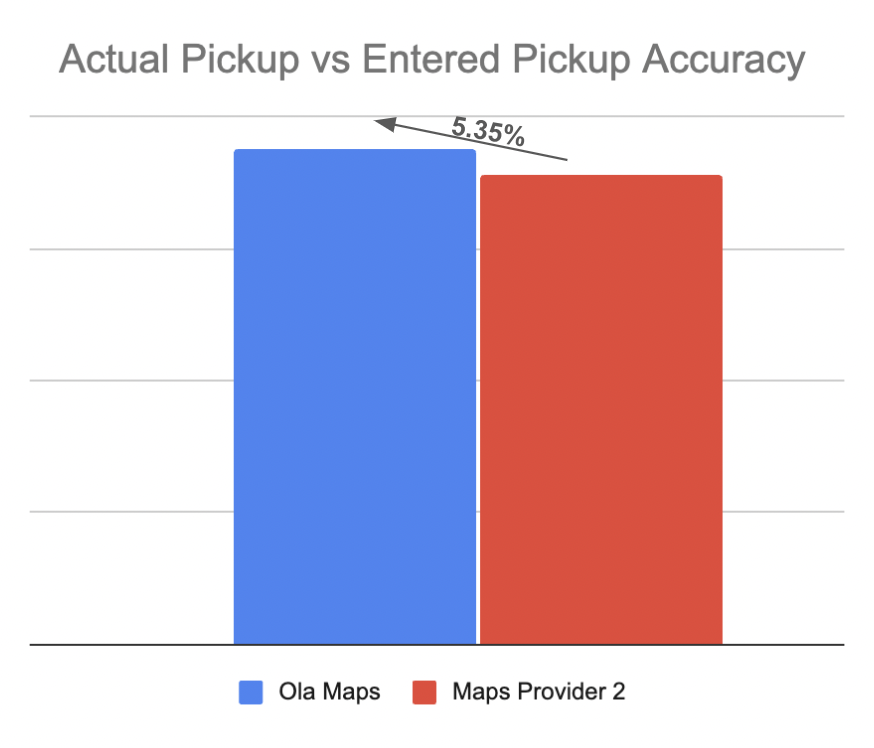
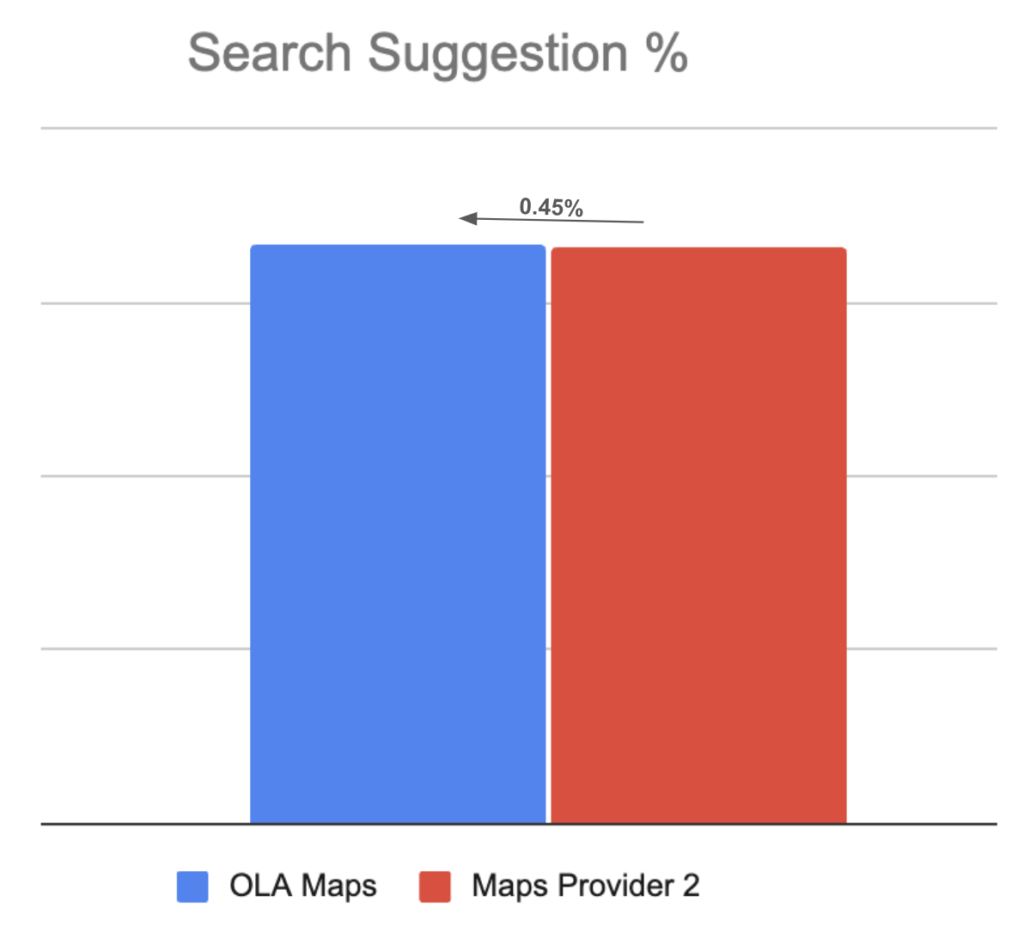
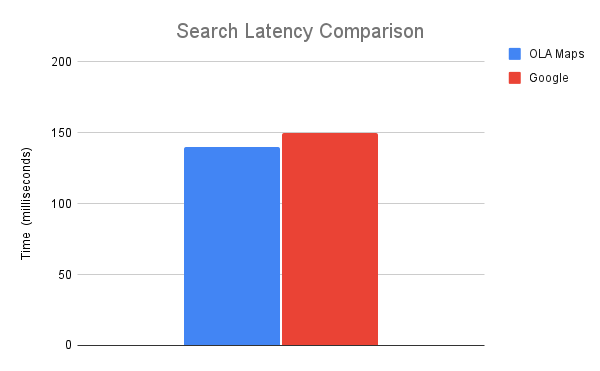
Metrics on Ola Maps performance since it’s launch in MoveOS4:
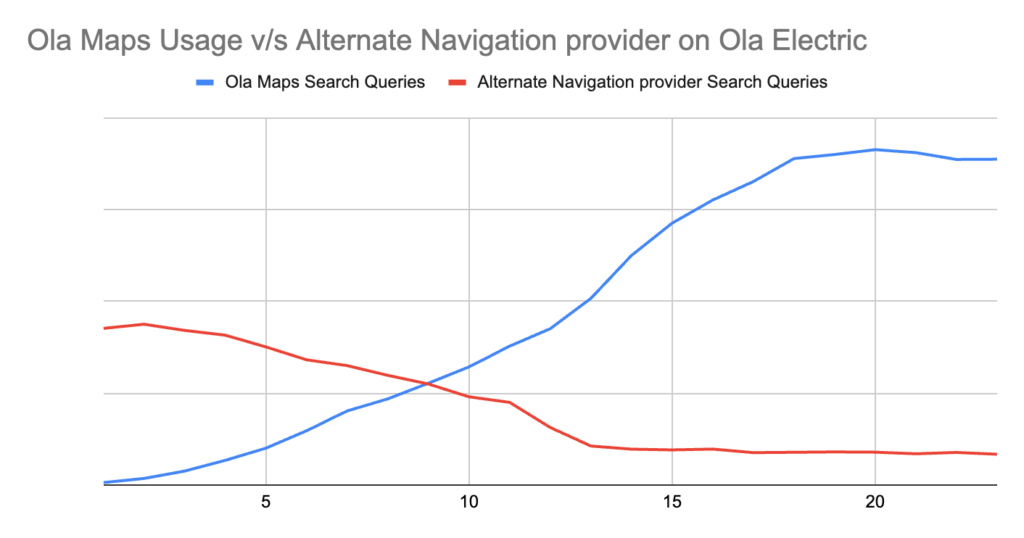
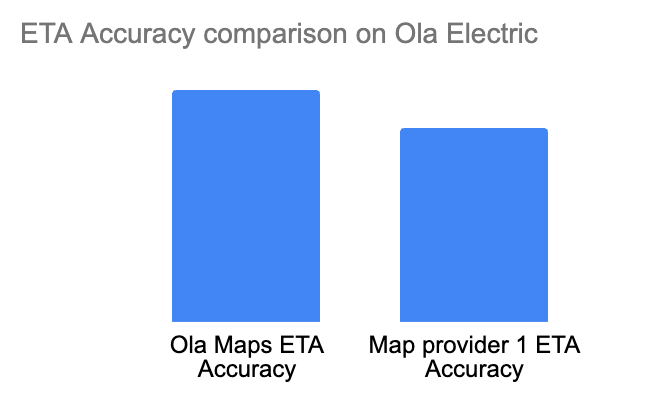

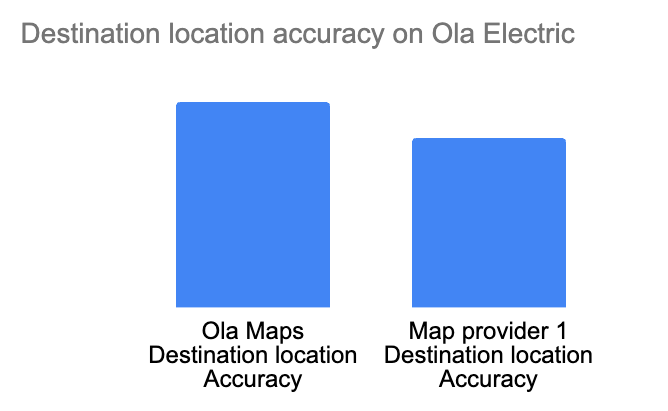
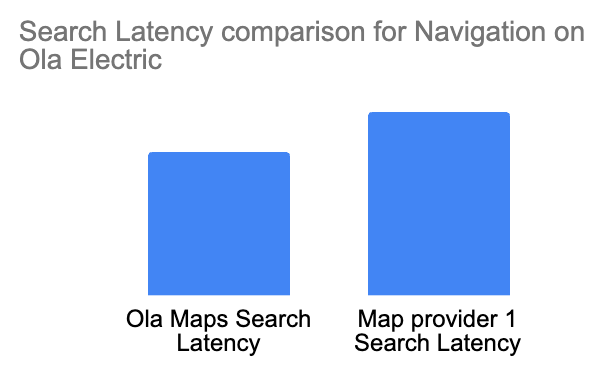
3.2 Mobility:
Our latest advancements in location technology have yielded impressive results, particularly in the accuracy of pickups and drop-offs. Here’s how we’re setting new standards in the industry:
- Pinpoint Pickups: Our enhanced pickup algorithm now outperforms the competition by a significant margin. Compared to competitors, we’ve achieved 5.3% better accuracy in matching actual pickup locations with the predicted ones and 5.1% on drops. This means less time waiting and searching, and more time getting to where you need to go.
- Lightning-Fast Results: We’ve turbocharged our search algorithm, achieving an impressive 6.67% reduction in response time. This means you’ll see available rides even faster, helping you get on the road sooner.
- Abcx – – – – – – – – –

Comprehensive Pickup Information: We’ve enriched the pickup experience by providing users with more detailed information with traffic polyline and traffic lights.
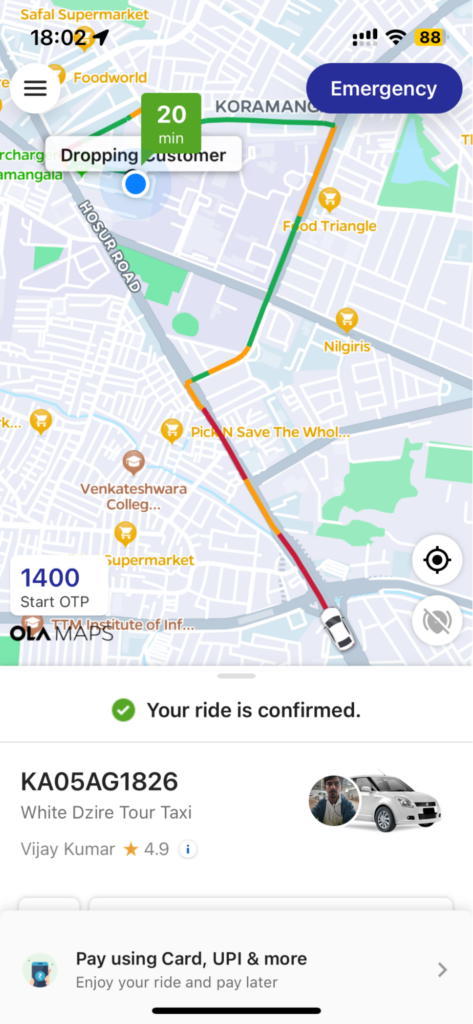
Traffic Polyline and Traffic lights

Fuzzy Search

In-App Navigation

3. Ola Maps APIs:
We are not democratizing the access to our ola maps core mapping apis for everyone though https://maps.olakrutrim.com/. These APIs are tailored to enhance location-based services with precision and efficiency for the Indian market:
- Directions API – Provides accurate routing and navigation, generating optimized routes with detailed turn-by-turn directions, travel times, and alternative routes for effective journey planning.
- Autocomplete API – Enhances search functionality by suggesting relevant completions in real-time for user queries. Ideal for connected cars, micro-mobility services, and delivery apps, it integrates location search capabilities for addresses, places, and points of interest.
- Geocoding API – Converts human-readable place names and addresses into geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). Suitable for mapping services, logistics platforms, and location-based applications.
- Reverse Geocoding API – Translates geographic coordinates into human-readable place names, including street addresses and broader areas. Useful for applications requiring accurate location data, such as GPS tracking systems.
- Last but not least
In doing so all the things we did to build Ola Maps, our cost of maps with external providers is zero!

Mobility mapping cost

Electric mapping cost.
Stay tuned for our deep dive into the world of Ola Maps in our upcoming installments where we’ll explore the intricate data foundations, cutting-edge AI applications, and our vision for the future of mapping technology. Don’t miss these insights into how we’re reshaping the landscape of location-based services.
Annexure:
The below part is what Chandra wanted to add in the Introductory section
Furthermore, existing maps do not fully address unique challenges related to delivering a seamless experience for Indian users and the opportunity it creates for Ola and Indian developers.
Challenges
- Incomplete Mapping Coverage: Many streets and rural areas are not mapped or poorly mapped.
- Inconsistent and Varying Street Names: Street names often have variations and inconsistencies, leading to confusion.
- Frequent Changes in Road Networks: New streets are created, and existing ones are closed frequently, leading to outdated maps.
- Traffic and Road Condition Variability: Traffic patterns are highly inconsistent, and road conditions vary significantly due to potholes and non-standard streets.
- Non-Standardized Streets: Many streets do not conform to standard measurements and layouts.
- Potholes and Road Quality Issues: Potholes and road quality can significantly affect travel time and safety.
Opportunities
- Enhanced User Experience: Providing accurate and up-to-date maps can significantly enhance navigation and travel planning, improving user satisfaction.
- Localized Features: Offering features tailored to local needs, such as multi-language support, local business listings, and culturally relevant landmarks.
- Smart Navigation Systems: Developing smart navigation systems that can suggest optimal routes based on real-time data, considering traffic, road conditions, and user preferences.
- Integration with Smart City Initiatives: Collaborating with smart city projects to integrate mapping data with other urban infrastructure, enhancing overall city management and services.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Navigation: Utilizing AR to provide intuitive and immersive navigation experiences, especially in complex urban environments.
- Real-time Predictions: Using state of the art time series models to foresee traffic congestion, road closures, and other disruptions, offering proactive routing suggestions.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with local communities to crowdsource map updates and feedback, ensuring the map remains relevant and accurate.
- Eco-friendly Routing: Implementing eco-friendly routing options that minimize fuel consumption and emissions, appealing to environmentally conscious users.
- Real-time Data Updates: Implementing real-time data updates through IoT devices, GPS tracking, and user-reported changes can keep maps current.
Addressing these unique challenges is not easy. In order to address and tap the opportunities, we are leveraging the power of AI by developing and using state of the art Krutrim models for delivering contextually relevant, accurate, safer and enhanced customer experience.What’s even more exciting is that we’re doing this from India, leveraging the country’s vast pool of tech talent to create cutting-edge mapping technology at a fraction of the cost. This approach not only allows us to be more efficient but also ensures that our maps are built with a global perspective from the ground up.